General
Getting Started with Building an Arduino
- What is the voltage rating of the capacitors?
- What is the difference between tx and txd? What is the difference between rx and rxd?
- What is the IC base type?
- What resistors go where?
- LED polarity?
- Is a quartz’s oscillator polarized?
- Is a push-button polarized?
- What’s up with header pins?
- Can I use a multilayer ceramic capacitor instead of a ceramic disc capacitor with the same capacitance?
- Credits
What is the voltage rating of the capacitors?
The voltage rating of a capacitor is simply the amount of voltage a particular capacitor is capable of handling. It’s okay to use capacitors with a higher rating - wasteful design implementation withstanding. On the other hand, it’s never okay to use a capacitor rated less than the circuit’s max voltage.
What is the difference between tx and txd? What is the difference between rx and rxd?
The difference is well nothing. Both are the same and perform the same things.
\(TXD = TX = Transmit\) \(RXD = RX = Receive\)
What is the IC base type?
For this project the IC holder is the narrow 28 Pin variant. This is the same structure as the ATMEGA328P-PU chip.
What resistors go where?
Please see the attached picture of the schematic. At first, this may be daunting but after understanding the circuit and PCB it will be easy to know what goes where. It’s important to understand why certain components were used and what purpose they serve.
LED polarity?
This webpage will help
Is a quartz’s oscillator polarized?
No, quartz’s oscillators do not have any polarity and can be connected anyway.
Most quartz’s oscillators have their rating etched on the top try to orient in such a way that all components can be read when looking at the board in one direction.
Is a push-button polarized?
Again, push-buttons are also not polarized. To help understand how a push-button works please have a look at the GIF below.
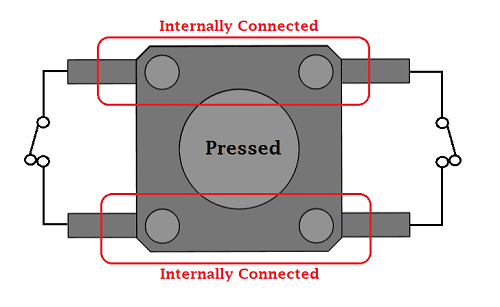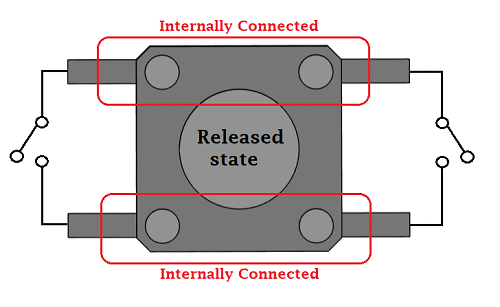
Credit: Components101
What’s up with header pins?
Header pins particularly female header pins in our experience were very difficult to get to specification. For example, if the layout needed only 10 pins the pins would need to be cut. The problem is that female headers never cut properly in a straight line. They either chip or cut slanted, especially when using a plier cutter/ scissor. Male headers have clear indentations after every pin so it’s easy to put them relatively straight.
One of the most frustrating parts is cutting the wrong number of pins. Triple check the number of pins needed and the number being cut!
For female header pins (especially if this is your first time) we suggest cutting one extra pin from the number needed. This is because if cut wrongly the last will break off. If this happens with one extra pin, then it’s easy to remove that pin and sand down the extra part to make a smooth professional finish.
Can I use a multilayer ceramic capacitor instead of a ceramic disc capacitor with the same capacitance?
Ceramic disc capacitors pick up and introduce vibration as a signal into your circuit. Most ceramic capacitors do this in a limited manner, but multilayer ceramic capacitors are worse than disc capacitors. Other than this small technicality (for this circuit) you can substitute one for the other.